
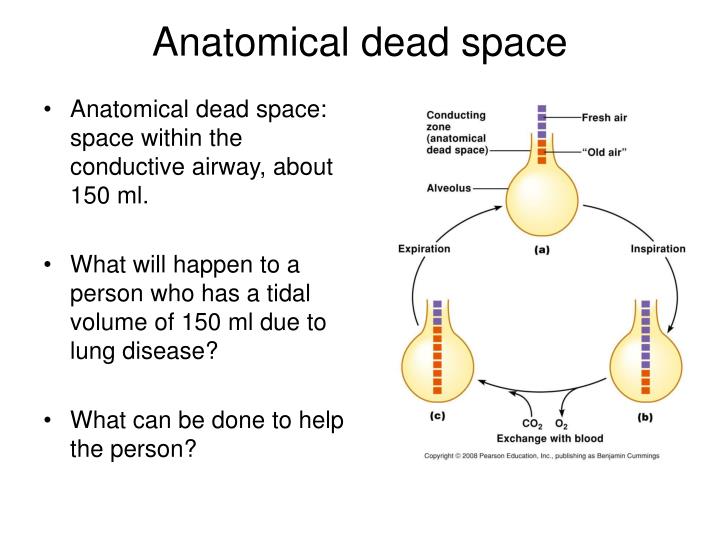
Insufficient pulmonary surfactant in the alveoli can contribute to the collapse of a lung.Great alveolar cells secrete pulmonary surfactant to lower the surface tension of water to maintain the lungs elastic recoil.In some alveolar walls there are pores between alveoli called pores of Kohn. The alveoli consist of an epithelial layer and an extracellular matrix surrounded by capillaries.Carbon-dioxide-rich blood is pumped from the rest of the body into the alveolar blood vessels where, through diffusion, it releases its carbon dioxide and absorbs oxygen.

The alveolar membrane is the gas-exchange surface.The pulmonary alveoli are the terminal ends of the respiratory tree that outcrop from either alveolar sacs or alveolar ducts both are sites of gas exchange.An alveolus is an anatomical structure that has the form of a hollow cavity and is found in the lung parenchyma ( tissue inside the lung).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
